The growth of 1D materials such as carbon nanotubes offers the potential for their use in new applications such as: improving the proporties of paint; biosensors and fine filters. Instruments provides process solutions for a wide variety of 1D materials growth.
Growth of inorganic nanowires as well as carbon nanotubes with in situ catalyst preparation and activation.
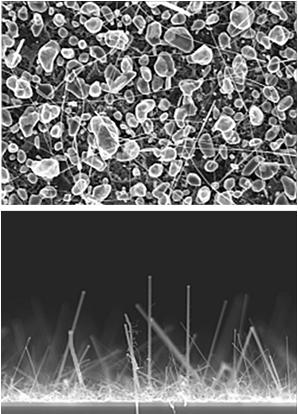
ZnO nanowires and nanorods are good candidates for nanometre scale electronic applications, such as sensors or emission transistors, because of their sensitivity to the chemical environment. The sensing process is related to oxygen vacancies on the that influence the electronic properties of ZnO.
ZnO nanowires and nanorods are also potentially good candidates for nanometre scale photonic device applications, ultraviolet photo-detectors and light emitting devices. Both p-type ZnO nanowires and n-type ZnO nanowires can be produced as positively and negatively charged semiconducting materials, this forms good foundation to make light emitting diodes (LED), in which, as an electron meets a hole, it falls into a lower energy level and releases energy in the form of a photon of light.
ZnO nanowires and nanorods can be used for fabrication of solar cells that can be dye-sensitised using liquid or solid (hole conductor) electrolyte, because ZnO has a wide bandgap, charge carrier mobility and can give a area for efficient dye-sensitization and light harvesting.
ZnO nanowires and nanorods can promote catalyst reactions with light as energy source, i.e. they can be used as photocatalysts.
The biocompatibility of ZnO nanowires and nanorods along with their electro-optical properties makes them suitable for active biomedical devices.
 公安机关备案号31010402003473
公安机关备案号31010402003473
